herbal books
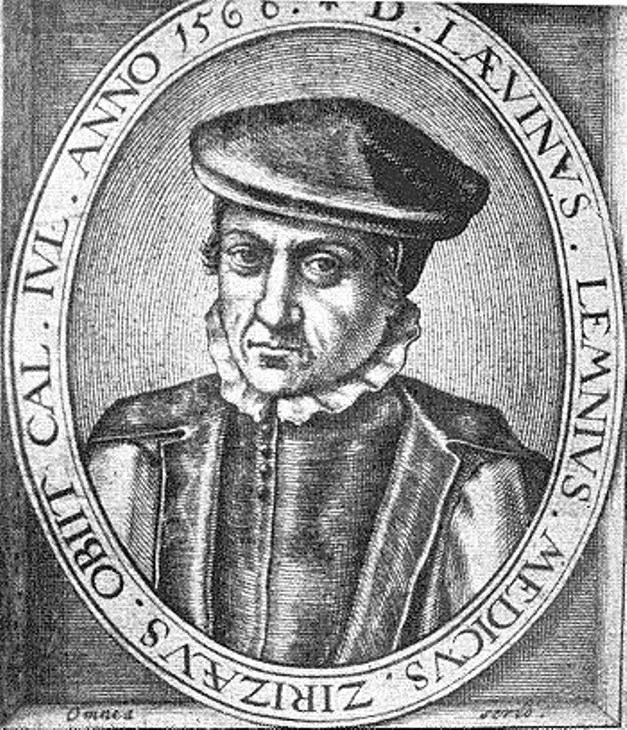

Levinus Lemnius (Dutch: Lieven Lemse, Lenneus, Lennius, Lemmens, Lemnii of Lemnes) was a Dutch physician, philosopher, botanist and writer.
He studied under the famous Swiss botanist and bibliographer Conrad Gesner at the University of Louvain and under the famous Flemish anatomist Andreas Vesalius at the University of Padua. Lemnius's book On the Habit and Constitution of the Body was translated by Thomas Newton, an Anglican clergyman who translated some of Lemnius's treatises into English, as well as other modern continental and classical works.
Lemnius is considered the first author to describe the plants mentioned in the Bible, in T. Newton's translation, Herbal for the Bible (1587). Levin Lemnius's most famous book is Occulta naturae miracula (1559), a book of mysteries that was reprinted many times over a period of four hundred years.
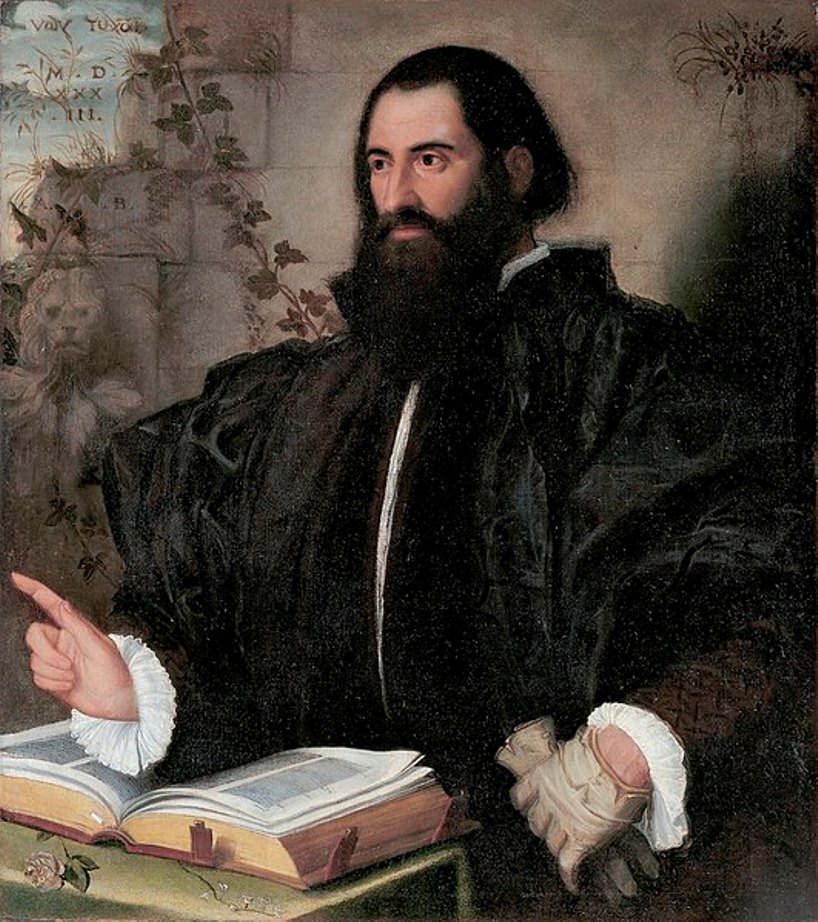


Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli was a 16th-century Italian physician, botanist and pharmacist.
Mattioli studied medicine in Padua and obtained a medical practice first in his hometown. Later, in the 1555-1560s, he served as personal physician to the imperial court of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria, and Emperor Maximilian II. This high position allowed him to test the effects of poisonous plants on prisoners for scientific purposes.
Mattioli published several scientific works in which he included many of his own observations on the flora of the Alps, including previously unexplored plants. These works, based on the study of books by predecessor scientists, gave impetus to the development of botany throughout Italy at the time. Mattioli kept up a lively correspondence with other researchers, describing specimens of rare plants received from them. The genus of flowering plants Matthiola is named after Mattioli.

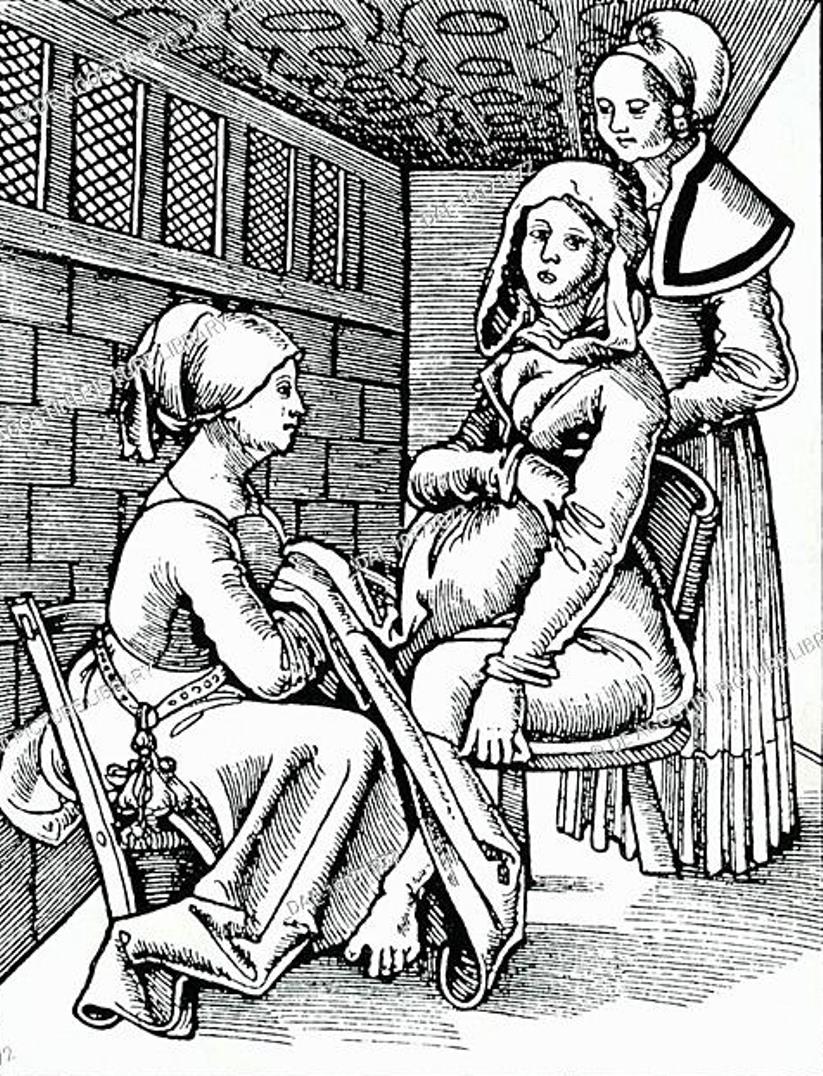
Eucharius Rösslin the Elder or Eucharius Rößlin was a German medieval scholar, physician-midwife, and pharmacist.
In 1493 Eucharius became apothecary in Freiburg, and 13 years later was elected physician of the city of Frankfurt am Main. From there he moved to Worms, in the service of Katherine, Princess of Saxony and Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg. One of his duties was to oversee and supervise the city's midwives, whose ignorance led to a high infant and female mortality rate.
In order to remedy this, Eucharius wrote and published a book on midwifery called Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden for Pregnant Women and Midwives") in Strasbourg in 1513. It was in German and contained several engravings. The book proved very popular and soon became the standard medical textbook for midwives. For nearly two centuries it was the authoritative guide to midwifery in Europe, translated into seven languages and reprinted over a hundred times.
In 1517 Rösslin returned to work in Frankfurt and remained in that position until his death in 1526. His son, also named Eucharius Rösslin, succeeded him as city physician.


Eucharius Rösslin the Elder or Eucharius Rößlin was a German medieval scholar, physician-midwife, and pharmacist.
In 1493 Eucharius became apothecary in Freiburg, and 13 years later was elected physician of the city of Frankfurt am Main. From there he moved to Worms, in the service of Katherine, Princess of Saxony and Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg. One of his duties was to oversee and supervise the city's midwives, whose ignorance led to a high infant and female mortality rate.
In order to remedy this, Eucharius wrote and published a book on midwifery called Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden for Pregnant Women and Midwives") in Strasbourg in 1513. It was in German and contained several engravings. The book proved very popular and soon became the standard medical textbook for midwives. For nearly two centuries it was the authoritative guide to midwifery in Europe, translated into seven languages and reprinted over a hundred times.
In 1517 Rösslin returned to work in Frankfurt and remained in that position until his death in 1526. His son, also named Eucharius Rösslin, succeeded him as city physician.


Eucharius Rösslin the Elder or Eucharius Rößlin was a German medieval scholar, physician-midwife, and pharmacist.
In 1493 Eucharius became apothecary in Freiburg, and 13 years later was elected physician of the city of Frankfurt am Main. From there he moved to Worms, in the service of Katherine, Princess of Saxony and Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg. One of his duties was to oversee and supervise the city's midwives, whose ignorance led to a high infant and female mortality rate.
In order to remedy this, Eucharius wrote and published a book on midwifery called Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden for Pregnant Women and Midwives") in Strasbourg in 1513. It was in German and contained several engravings. The book proved very popular and soon became the standard medical textbook for midwives. For nearly two centuries it was the authoritative guide to midwifery in Europe, translated into seven languages and reprinted over a hundred times.
In 1517 Rösslin returned to work in Frankfurt and remained in that position until his death in 1526. His son, also named Eucharius Rösslin, succeeded him as city physician.


Eucharius Rösslin the Elder or Eucharius Rößlin was a German medieval scholar, physician-midwife, and pharmacist.
In 1493 Eucharius became apothecary in Freiburg, and 13 years later was elected physician of the city of Frankfurt am Main. From there he moved to Worms, in the service of Katherine, Princess of Saxony and Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg. One of his duties was to oversee and supervise the city's midwives, whose ignorance led to a high infant and female mortality rate.
In order to remedy this, Eucharius wrote and published a book on midwifery called Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden for Pregnant Women and Midwives") in Strasbourg in 1513. It was in German and contained several engravings. The book proved very popular and soon became the standard medical textbook for midwives. For nearly two centuries it was the authoritative guide to midwifery in Europe, translated into seven languages and reprinted over a hundred times.
In 1517 Rösslin returned to work in Frankfurt and remained in that position until his death in 1526. His son, also named Eucharius Rösslin, succeeded him as city physician.


Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.


Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.


Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli was a 16th-century Italian physician, botanist and pharmacist.
Mattioli studied medicine in Padua and obtained a medical practice first in his hometown. Later, in the 1555-1560s, he served as personal physician to the imperial court of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria, and Emperor Maximilian II. This high position allowed him to test the effects of poisonous plants on prisoners for scientific purposes.
Mattioli published several scientific works in which he included many of his own observations on the flora of the Alps, including previously unexplored plants. These works, based on the study of books by predecessor scientists, gave impetus to the development of botany throughout Italy at the time. Mattioli kept up a lively correspondence with other researchers, describing specimens of rare plants received from them. The genus of flowering plants Matthiola is named after Mattioli.





Leonhart Fuchs was a German humanist scientist, botanist, and physician.
Fuchs received a humanistic education under Catholic guidance, but later became a Protestant. He studied medicine and became a professor in Tübingen. He was most interested in the medicinal properties of plants. Well acquainted with the Greek and Latin classics and an excellent observer, he gave precise descriptions, and his beautiful engravings of plants established the tradition of depicting plants with precise illustrations and in alphabetical order.
In 1542 Fuchs published his most important work, De Historia Stirpium Commentarii Insignes (Famous Commentaries on the History of Plants). The book was a great success, especially because of the magnificent woodcuts and the 487 plants, which were described for the first time in such a systematic form. De Historia Stirpium survived several editions and was translated into Dutch and German.
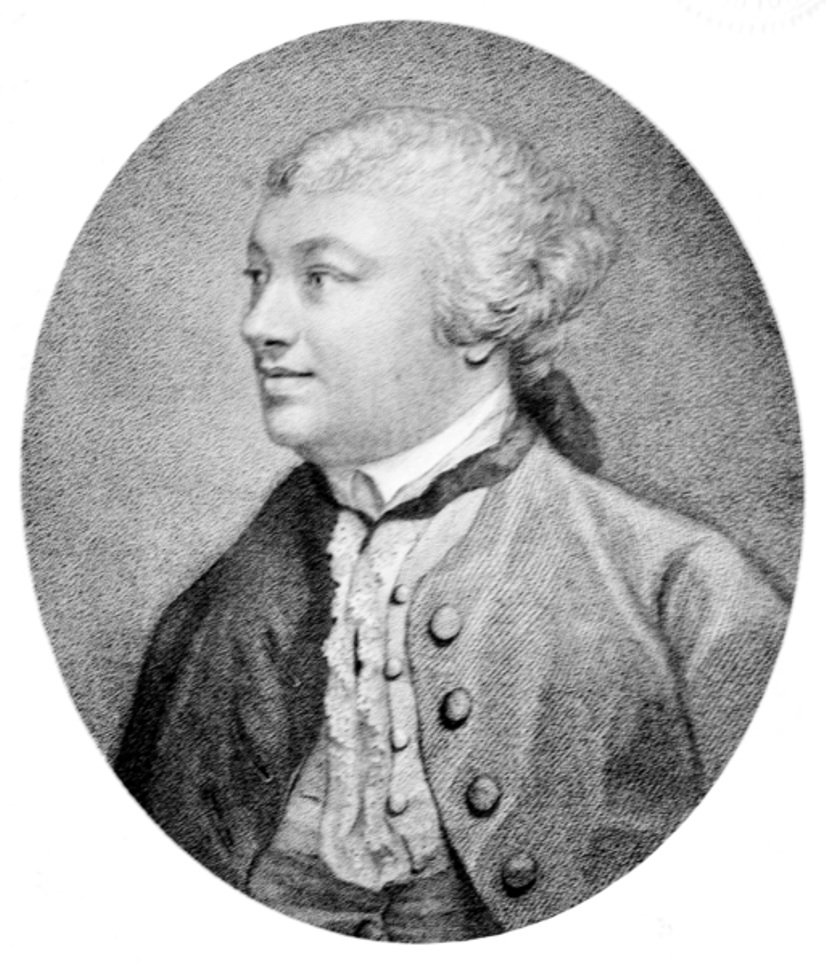


John Hill was a British botanist, pharmacologist and physician, geologist, writer and journalist.
Hill edited the monthly British Magazine for several years, and also wrote a daily society gossip column in The London Advertiser and Literary Gazette. His satirical, often on the edge of propriety articles were often the cause of scandals. Hill also wrote novels, plays, and scientific works on geology, medicine, philosophy, and botany.
In 1759, the first of the 26 volumes of his Plant System was published. This voluminous work contained descriptions of 26,000 different plants and 1,600 illustrations. For this long work, Hill received the Order of Vasa from the Swedish king and began calling himself Sir.

![[HERBAL]](/assets/image/picture_5108883/1dd2b/c148090935abcdf46909d404a61555bd1765321200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)
![[HERBAL]](https://veryimportantlot.com/assets/image/picture_5108883/1dd2b/c148090935abcdf46909d404a61555bd1765321200jpg__fix_374_244.jpeg)